Fight Inflammation
Natural remedies to reduce chronic inflammation.
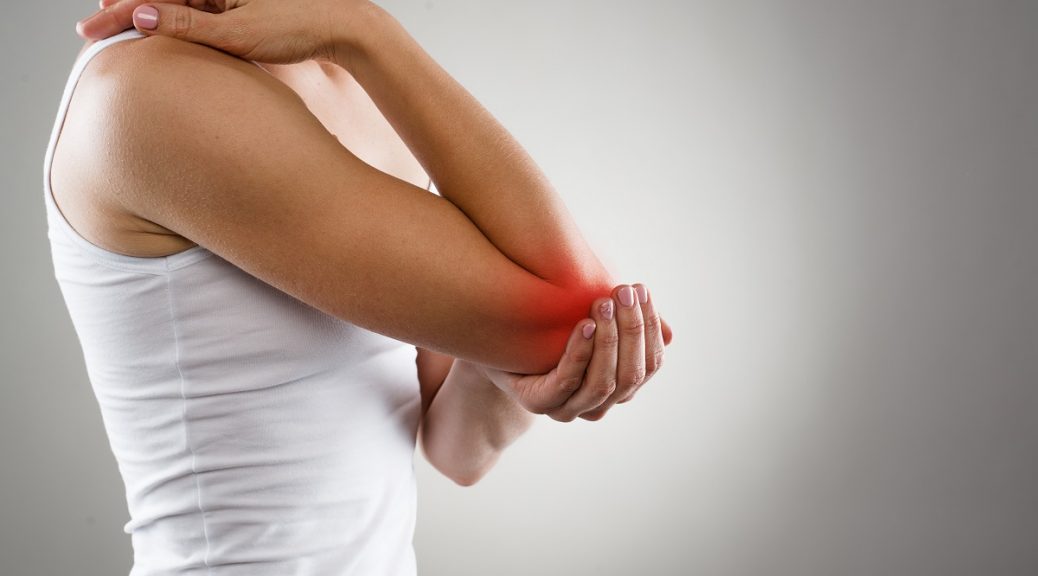
Inflammation is a word often associated with sore, painful and swollen joints, which are usually red in colour and hot to touch, but inflammation can occur anywhere in the body. People are often under this misconception that inflammation is a bad thing, but it’s not necessarily so.
Inflammation is a healing process, it’s your body’s attempt at self-protection. Inflammation occurs when your body is trying to kill any harmful stimuli, including irritants, pathogens and damaged cells, and is trying to heal the infection caused by it. It is simply the body’s immune system response.
“Inflammation is the body’s natural way of responding to stress, infection and illness, helping us to stay healthy,” confirms Chris Newbold, head of clinical nutrition at BioCare.
“Inflammation is a natural and necessary part of the immune system. It increases blood flow to damaged tissues and increases permeability of the smallest blood vessels – letting white blood cells and platelets through so they can heal cuts, burns and broken bones,” explains Wendy Richards, from So What Am I? (SWAMI).
She adds: “When there is too much inflammation in the body, damage can occur. The body thinks that some of its own cells are ‘non-self’ and need to be broken down. This can cause many chronic diseases, such as arthritis, heart disease, kidney disease and depression.”
Chronic and Acute Inflammation
There are two types of inflammation, acute and chronic. Acute inflammation lasts for a shorter period and is your body’s natural and helpful immune response to tissue damage, whereas chronic is long-term and is linked to a number of health issues.
Chronic inflammation is caused by your body’s failure to eliminate the stimuli that was causing acute inflammation, or in some conditions, it’s when the immune system attacks healthy tissue, mistaking it for harmful pathogens.
“Unless the root cause of the inflammation is addressed, symptoms are likely to persist to some extent and the risk of further health concerns may be increased,” comments Hannah Braye, nutritional therapist at Probiotics International Ltd (Protexin), manufacturers of Bio-Kult and Lepicol. “Identifying factors contributing to inflammation such as high stress levels, poor blood sugar regulation, hidden food intolerances, leaky gut, dysbiosis (an imbalance of bacteria in the gut), immune dysregulation, lack of sleep and poor diet and lifestyle habits, and addressing these, is therefore important.”
Support your Gut Bacteria
Many inflammatory processes have been found to stem from poor gut health. This is not surprising as 70 percent of our immune cells (which control the inflammatory response) reside within the lining of the gut and are supported by our beneficial gut bacteria.
“When this lining becomes damaged, due to low beneficial bacteria levels, stress, medications, or poor diet and lifestyle habits, it can become ‘leaky’, allowing endotoxins and larger food proteins to enter the blood stream,” explains Braye. “The immune system sees these as foreign invaders and mounts an inflammatory response against them, which can manifest in many systems of the body from the gut, to the skin and the brain.”
To help support the lining of the gut, Braye recommends bone broth and fermented foods: “Bone broth/stock contains numerous nutrients which help support the lining of the gut, helping to repair it. It’s best to use organic bones, and simmer on a low heat (for example in a slow cooker) for a number of hours. The health of the lining of the gut is also supported by our beneficial gut bacteria. Eating traditionally fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, live yoghurt and kefir is a great way to help support a diverse range of bacteria in the gut.”
Increase Omega-3
One of the nutrients with the most positive impact on inflammation is pure omega-3 fish oils.
“Omega-3 fatty acids found in oily fish, such as salmon, mackerel, anchovies, sardines and herring, hemp seeds, chia seeds and flax seeds are some of the most anti-inflammatory foods on offer,” explains Braye. “We should ideally be eating two to three portions of oily fish a week.”
“As the body does not produce omega-3 fatty acids, it’s important to ensure you get these from your diet or supplements,” agrees Newbold.
Focus on Fruit, Vegetables and Healthy Fats
“Those suffering from inflammatory conditions are best advised to follow an anti-inflammatory diet,” advises Braye. “This is a diet low in sugars, refined carbohydrates (and for some people grains in general) and processed foods, whilst eating lots of antioxidant foods such as colourful fruit, vegetables and herbs.”
“Eating more fruits, vegetables and whole grains is also a better way of getting your carbohydrates,” explains Newbold. “If you get the majority of your carbs from processed starches and sugar, this can contribute to metabolic dysfunctions, which contributes to inflammation. It is also important to eat the right fats, by eating unsaturated sources like avocados, nuts and olives; you can reduce your body’s inflammation levels.”
Choose Anti-Inflammatory Spices
Turmeric and ginger are both power anti-inflammatory spices, they work by inhibiting pro-inflammatory enzymes.
“Turmeric has been used as a powerful anti-inflammatory in Chinese and Indian medicine for millennia,” comments Richards. “Curcumin, the primary pharmacological agent in this spice, contains proven effects in this area that are comparable to over-the-counter anti-inflammatory agents as well as some prescription medications. Curcumin has powerful anti-inflammatory effects and is a very strong antioxidant.”
Try to Stress Less
“Stress leads to inflammation – adrenaline by its very nature is highly inflammatory and we can be making this 24/7, especially with the influence of caffeine and the sense of urgency and immediacy we now live with,” explains Richards.
“We then have to make cortisol because it’s an anti-inflammatory, and that has a massive flow-on effect to immune function, blood sugar regulation, body fat storage, the list goes on. Decreasing adrenaline is huge in stopping an inflammatory response.”
Try these:
BioCare – Mega EPA
Bio-Kult – Advanced Multi-Strain Formula